- 您現(xiàn)在的位置: 微波EDA網(wǎng) >> CST >> CST設(shè)計(jì)實(shí)例 >> 正文
CST同軸線器件的仿真設(shè)計(jì)分析—CST2013設(shè)計(jì)實(shí)例
Define Boundary Conditions and Symmetries
Before you start the solver, you should always check the boundary and symmetry conditions. This is most easily accomplished by entering the boundary definition mode by selecting Simulation: Settings Boundaries . The boundary conditions will then become visualized in the main view as follows:
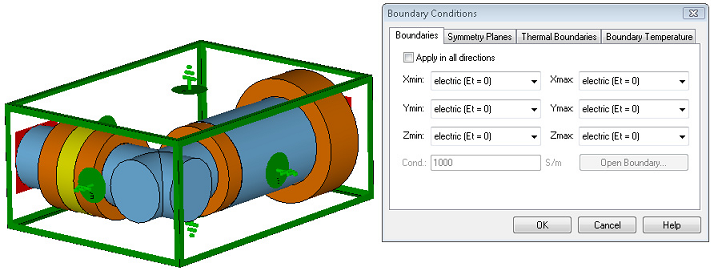
Here, all boundary conditions are set to electric which means that the structure is embedded in a perfect electrically conducting housing. These defaults are appropriate for this example.
Due to the structures symmetry to the XY plane and the fact that the magnetic field in the coaxial cable is perpendicular to this plane, a symmetry condition can be used. This symmetry reduces the time required for the simulation by a factor of two.
Please enter the symmetry plane definition mode by activating the Symmetry Planes tab in the dialog box. By setting the symmetry plane XY to magnetic, you force the solver to calculate only the modes that have no tangential magnetic field component on these planes (thereby forcing the electric field to be tangential to these planes).The screen should then look as follows:
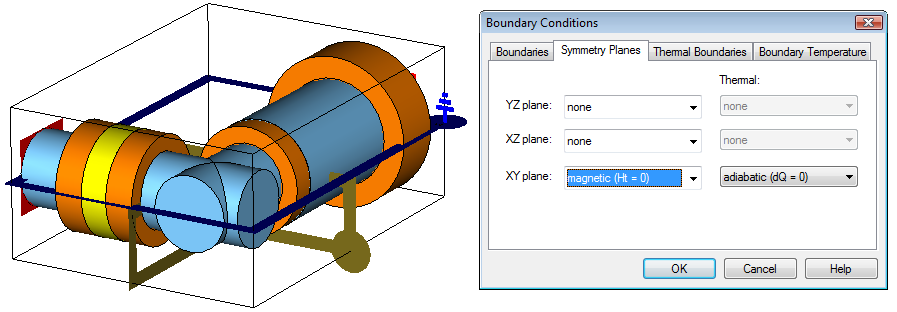
Please note that you also could double-click on the symmetry planes handle and choose the proper symmetry condition from the context menu.
Finally, press the OK button to complete this step.
In general, you should always make use of symmetry conditions whenever possible to reduce calculation times by a factor of two to eight.
Define the Frequency Range
The frequency range for the simulation should be chosen with care. Different considerations must be made when using a transient solver or a frequency domain solver (see next chapter for details).
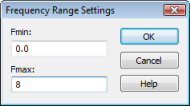
For this example, we will choose a frequency range from 0 to 8 GHz. Open the frequency range dialog box Simulation: Settings Frequency and enter the range of 0 to 8 (GHz) before pressing the OK button (the frequency unit has previously been set to GHz and is displayed in the status bar):
Define Field Monitors
CST MICROWAVE STUDIO uses the concept of monitors to specify which field data to store. In addition to choosing the type, you can also specify whether the field is recorded at a fixed frequency or at a sequence of time samples (the latter case applies only to the transient solver). You may define as many monitors as necessary to obtain the fields at various frequencies. For the transient solver, all monitors are calculated from a single simulation run by the Fourier Transform. Consequently, the computational overhead for a defined monitor is relatively small.
Please note that an excessive number of field monitors may significantly increase the memory space required for the simulation.
Assume that you are interested in the current distribution on the coaxial cables conductors at several frequencies (2, 4, 6 and 8 GHz). To add field monitors, select Simulation: Monitors > Field Monitor .
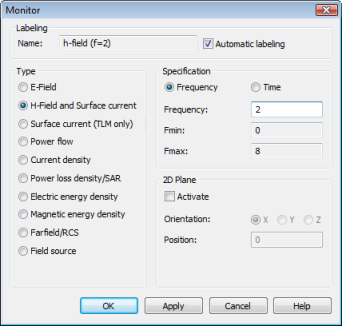
In this dialog box, you should first select the Type H-Field/Surface current before specifying the frequency for the monitor in the Frequency field. Afterwards, press the Apply button to store the monitors data. Please define monitors for the following frequencies: 2, 4, 6, 8 (with GHz being the currently active frequency unit). Please make sure that you press the Apply button for each monitor (the monitor definition is then added in the Monitors folder in the navigation tree).
After the monitor definition is completed, you can close this dialog box by pressing the OK button.
-

CST中文視頻教程,資深專家講解,視頻操作演示,從基礎(chǔ)講起,循序漸進(jìn),并結(jié)合最新工程案例,幫您快速學(xué)習(xí)掌握CST的設(shè)計(jì)應(yīng)用...【詳細(xì)介紹】
- CST天線設(shè)計(jì)和天線陣設(shè)計(jì)—CST2013設(shè)計(jì)實(shí)例
CST諧振腔體設(shè)計(jì)分析—CST2013設(shè)計(jì)實(shí)例
使用CST微波工作室進(jìn)行TDR計(jì)算分析
CST與Matlab連接設(shè)置
CST微波工作室和Agilent ADS 協(xié)同仿真連接設(shè)…
CST微波工作室查看VSWR結(jié)果
CST仿真分析結(jié)果如何與外部數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行比較
CST微波工作室采用的主要算法
使用CST微波工作室的時(shí)域求解器仿真電大問題…
電磁兼容的數(shù)值仿真分析——CST2013
CST仿真性能和仿真技術(shù)
CST設(shè)計(jì)環(huán)境 — CST2013
推薦課程
-
7套中文視頻教程,2本教材,樣樣經(jīng)典
-
國內(nèi)最權(quán)威、經(jīng)典的ADS培訓(xùn)教程套裝
-
最全面的微波射頻仿真設(shè)計(jì)培訓(xùn)合集
-
Ansoft Designer 學(xué)習(xí)培訓(xùn)課程套裝
首套Ansoft Designer中文培訓(xùn)教材
-
矢網(wǎng),頻譜儀,信號源...,樣樣精通
-
與業(yè)界連接緊密的課程,學(xué)以致用...
-
Les Besser射頻培訓(xùn)經(jīng)典原版視頻
業(yè)界大牛Les Besser的培訓(xùn)課程...
-
PCB設(shè)計(jì)學(xué)習(xí)培訓(xùn)課程套裝
Allegro,PADS,PCB設(shè)計(jì),其實(shí)很簡單..
-
Hyperlynx,SIwave,助你解決SI問題
-
現(xiàn)場講授,實(shí)時(shí)交流,工作學(xué)習(xí)兩不誤






